Papillomas are classified as benign neoplasms that look like warts protruding on the skin. Such growths not only cause cosmetic discomfort, but under certain circumstances can cause harm to human health and even become malignant.
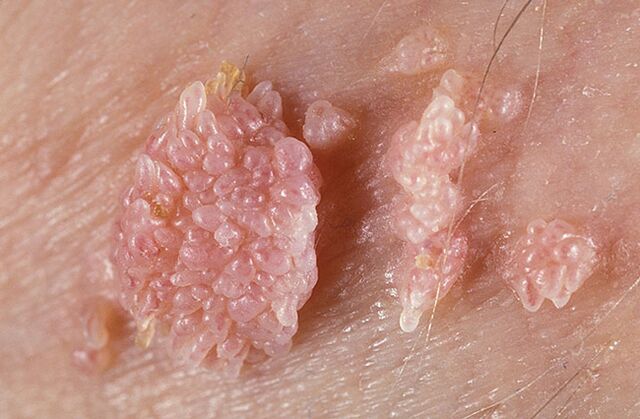
Why do papillomas appear and how to eliminate them without harming health?
What papillomas look like: varieties and types
Small benign formations (up to several millimeters in diameter) may appear on the skin and mucous membranes, which in the people are called "warts", and in medicine – papillomas. The growths are soft to the touch, have a slightly convex shape and hang slightly, and their surface is heterogeneous and varies depending on the type of papillomas.
Where papillomas can occur:
- On the feet and hands;
- On the face and neck;
- On the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- In the nasopharynx and oral cavity;
- In the armpit area;
- In the urethra.
Most often, papillomas are localized and spread on the genitals.
Important!The main and only cause of papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
According to the degree of risk to human health, papillomas are divided into two types:
- With low level– papillomas caused by HPV types 6 and 11;
- With a high level– neoplasms that appear under the influence of the HPV virus types 18, 31, 16, 35 and 33; the risk of developing dysplasia and cancer with such tumors is quite high.
Papillomas are a fairly common phenomenon and appear with the same frequency in both men and women. With a healthy immune system and a healthy lifestyle, the papilloma virus can "live" in the human body for many years without being recognized. But when the body weakens under the influence of certain factors, HPV begins to manifest itself externally: growths appear, redness and irritation may occur on the mucous membranes.
Important!Papillomas are not a malignant formation, but some varieties can create favorable conditions for the development of precancerous conditions and cancer.
There are many types of papillomas, depending on the type of HPV that has entered the body.
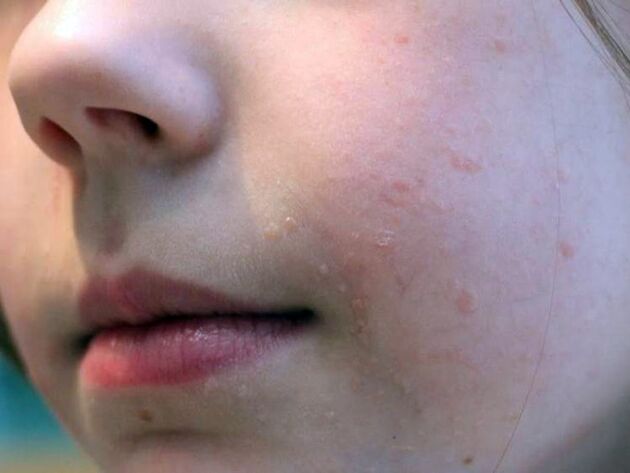
How do the main types of papillomas appear:
- Warts are flat– round or oval warts that rise above the skin by 1-2 mm. They are found in adolescents and young adults, which is why they are also called "juvenile warts. "
- Warts are simple ("vulgar")– they rise about 2-3 mm above the skin and occur most often on the feet, palms and hands and are rough to the touch.
- Condylomata acuminata– looks like a cockscomb or cauliflower. Most often they are found on the mucous membranes: in the urethra, genitals and mouth.
- Filiform warts– very often this type is called "papillomas" and are typical for people over the age of 35-40. They are most often located in the armpits, on the face and neck, and under the breasts in women. The dimensions do not exceed 3-5 mm and appear as round or thread-like growths.
Less common are papillomas in the urethra and bladder, usually in men and in combination with genital warts. A separate group includes papillomas in the larynx, trachea and oral cavity, becauseSuch neoplasms cause a lot of problems to the patient and in some cases even pose a threat to life.
Why do papillomas occur?
The cause of papillomas in humans is HPV, which, penetrating the blood, begins to actively multiply, affecting mainly the upper layers of the skin. With strong and strong immunity, the external manifestations of the virus may not be observed for quite a long time, but under favorable conditions the pathological growth of the epithelium begins.
Usually the incubation period does not exceed 2-3 months, but it happens that the latent course continues for several years.

The factors that cause the appearance of papillomas are:
- Decreased immunity– under the influence of past infections, stress, long-term illnesses, lack of vitamins.
- Bad habits– Smoking and alcohol abuse quite often cause tumor processes.
- Promiscuity– papillomas are often sexually transmitted and concomitant diseases of the reproductive system only favor the development of HPV.
Indirect causes of the development of HPV can be long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs for viral and infectious diseases and gastrointestinal pathologies.
Important!HPV infection occurs through sexual contact in 50% of cases. Therefore, doctors consider any person who is actively sexually active to be at risk.
Papillomas often appear in adolescence and young adulthood, which coincides with the onset of sexual activity. Young people are more likely to have unprotected sex and to change sexual partners. In this case, HPV can enter the body through the vaginal, oral and anal routes.
In women, the factors that provoke the appearance of papillomas are: a general weakening of the immune system (with long-term diseases, frequent stress), the use of oral contraceptives and menstrual irregularities.
In men, papillomas occur due to a promiscuous and active sexual life, refusal of condoms, nicotine and alcohol addiction.
How you can get infected:
- Sexually- the most common route of infection. Using a condom does not eliminate the risk of infection, especially if the growths are located in the perineum or anus.
- During pregnancy and childbirth– if a mother is infected with the HPV virus, it will pass to the baby during birth or through breast milk.
- With everyday transport– when using general hygiene products, in violation of health regulations.
Papilloma virus autoinfection often occurs in places with high humidity: on beaches, in swimming pools, in saunas. With minor damage to the skin or when the mucosa comes into contact with a source of HPV, infection occurs.
Penetrating into the organism, the virus finds the most favorable habitat for itself, but is more often localized in those parts of the body that are most often subject to microtraumas. The virus becomes contagious immediately after entering the human body. HPV does not spread to other organs, but it is quite difficult to get rid of it and it is almost impossible to completely eliminate the virus.
How to get rid of papillomas
Usually, papillomas do not require treatment if they do not cause cosmetic discomfort and are not subject to constant injury. Some rashes may disappear completely on their own when a person's immune strength increases, but with any provoking factor they reappear.
It is necessary to treat papillomas only in case of large growths and in the presence of risk factors for their degeneration into malignant tumors.
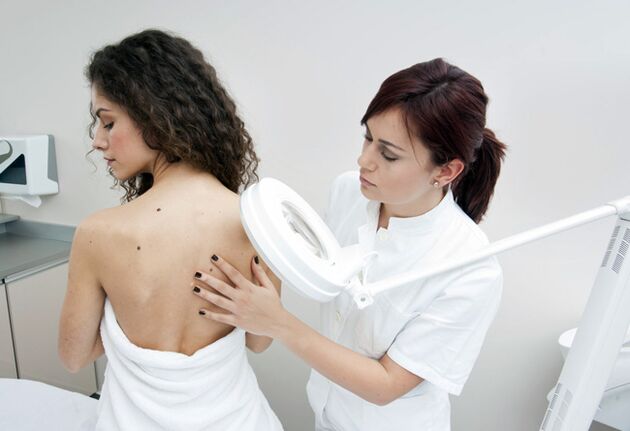
Home treatment is best carried out after consulting a doctor: most often the removal of papillomas is performed by a dermatologist; if the growths are located in the genital area, a dermatovenerologist (for men), a gynecologist (for women).
Important!Under no circumstances should you cut, scrape or squeeze tumors yourself!
Therapy for papilloma is carried out comprehensively: first, drugs that improve immunity and antiviral agents are prescribed. This is usually enough for the growths to disappear on their own.
But if papillomas interfere with a person's normal life or the doctor believes that the virus poses a danger to the patient's health and life, surgical removal of papillomas is proposed.
Note!It is impossible to completely eliminate the papilloma virus, but it is possible to remove papillomas at home or in the clinic, thereby preventing the dangerous development of the disease.
An infected person will need to take preventive measures to prevent the appearance of growths, adhere to a healthy lifestyle and strengthen immunity.
Treatment in clinic
Treatment in the clinic involves the removal of papilloma by surgical methods, and the method of elimination is chosen by the doctor based on the type of tumor and after diagnostic procedures.
It is usually recommended to remove the growth if the diameter of the tumor is more than 1 cm or if cancer is suspected. During the operation, growths and a certain amount of surrounding tissue are removed, after which cosmetic stitches are applied.
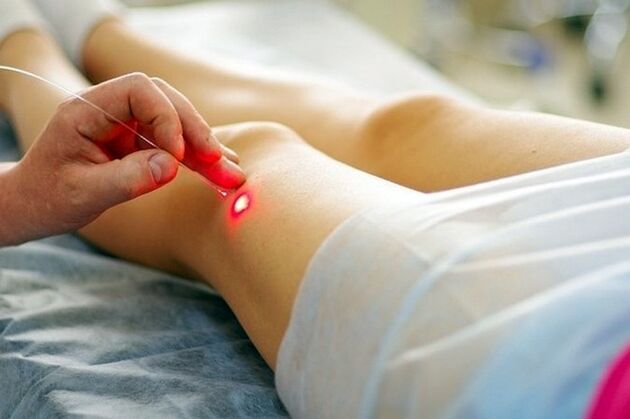
Surgical methods to remove papilloma:
- Laser removal.The most accessible and common method is to remove the growth with a laser after anesthesia with an anesthetic. The procedure takes approximately 20-30 seconds per tumor. After cauterization, a crust remains on the skin that cannot be removed: after a few days it will fall off on its own. In this way it is proposed to remove papillomas on the neck, face, armpits, under the mammary glands, where the skin is very delicate and is easily injured.
- Radiosurgical treatment.According to the principle of implementation, this method is similar to laser excision, but its distinctive advantage is that radio wave therapy is not so dangerous for human eyes and therefore is preferable when removing papillomas on the eyelid and face.
- Cryodestruction– cold cauterization using a cotton ball soaked in liquid nitrogen (liquid nitrogen has a temperature of minus 15 degrees). The frozen growth falls off on its own after a few days. The procedure does not require anesthesia, but it is not recommended to perform it on the face because treatment with liquid nitrogen can cause temporary redness of the skin.
- Electrocoagulation– an outdated method that uses an electric knife that burns tumors using high-frequency currents.
- Excision with scalpel– a previously common method of removing papillomas, now not used in almost all clinics due to the high risk of skin trauma.
The excised growth is sent for histological examination to exclude the presence of malignant cells.
The treatment does not end after the operation: the doctor prescribes the patient immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs and gives recommendations for carrying out medical procedures at home.
To increase immunity, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes, immunomodulators, diet, walks in the fresh air and hardeners.
After surgical removal, recurrences usually do not occur; Growths may reappear at the excision site if the area has not been completely cleaned.
Treatment at home
Some types of papillomas can be eliminated at home using folk and pharmaceutical remedies.
Removal of papillomas at home can be carried out using pharmaceutical products with cauterizing properties.
These drugs are composed of alkalis and acids, that is, they eliminate papillomas by burning tissues on the skin. Therefore, before cauterizing a papilloma at home, it is advisable to consult a doctor and use such products with caution so as not to damage the skin, especially if the growths are located on the face or neck.
Removal of papillomas at home should be carried out in compliance with three basic rules:
- You cannot remove genital warts from your genitals on your own.
- It is impossible to remove growths of an unknown nature with signs of bleeding, inflammation or overgrowth.
- It is not possible to remove tumors on the face - a scar or scar may remain, which the doctor will not be able to remove later.
How to get rid of papillomas at home:
- Garlic.Cut a piece of garlic and apply fresh juice to the growth, fix it with an adhesive plaster. Repeat twice daily for 2-4 weeks.
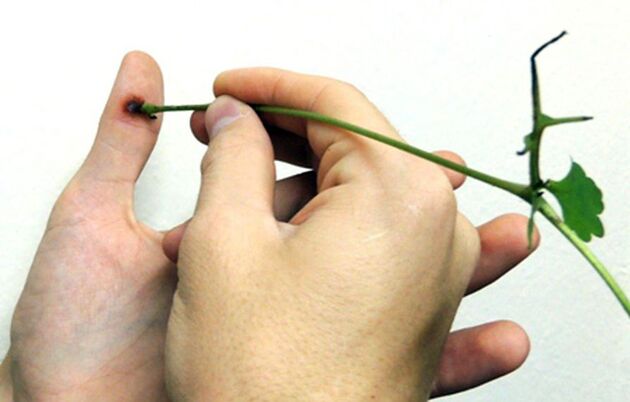
- Celandine juice.Make a cut from the stem of the celandine and apply the place where the juice is released on the new growth. You can carry out the procedure 2-3 times a day, from 14 to 30 days. This method allows you to quickly and painlessly remove papillomas on the face at home.
- Laundry soap.Soap your skin several times a day in the area where there are growths. Treatment is not effective for old and multiple tumors.
- Castor oil.The area around the papillomas is lubricated 1-2 times a day for 1-1. 5 months.
- Vinegar.You can mix 70% vinegar and glycerin in equal proportions and rub them on the growths three to four times a day. Or use ordinary 5% vinegar to lubricate the papilloma every day.
You can remove papilloma on the eyelid at home using Kalanchoe or aloe juice, simultaneously using antiviral ophthalmic drugs. But if the growth is located near the mucous membrane of the eye and inside the eyelid, it is better not to do home treatment, you need to consult an ophthalmologist or dermatologist.

The most gentle method of removing armpit papillomas at home is to use ordinary egg white: egg white is applied to the papilloma in a thick layer and left in this state for several hours, after which another layer is applied on top. After several days of repeating the procedure daily, the small papillomas dry up and fall off on their own.
Traditional medicine offers many ways to remove papillomas at home, but it should be borne in mind that different methods will be effective for different types and varieties of growths, so each method is purely individual and it is advisable to use it after consultation with a doctor.
Important!Various food supplements for papillomas, monastery tea, tea for parasites and papillomas - they do not help in the treatment of papillomas!
It is almost impossible to avoid HPV infection: even strictly adhering to the rules of personal hygiene, avoiding casual sex and visiting public places, there is no guarantee that the virus will not enter the body through contact with household objects previously touched by an already infected person.
Therefore, the main preventive measure for the occurrence of papillomas can be considered only increasing immunity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding stress and infectious diseases, taking vitamins and elimination of bad habits.
















